Bresenhams Line Generation Algorithm 23-03-2020
Instruction: First of all carefully watch video lecture then read theory.
Video Lecture: Bresenhams Line Algorithm
Video Lecture: Bresenhams Line Algorithm
This algorithm is used for scan converting a line. It was developed by Bresenham. It is an efficient method because it involves only integer addition, subtractions, and multiplication operations. These operations can be performed very rapidly so lines can be generated quickly.
In this method, next pixel selected is that one who has the least distance from true line.
The method works as follows:
Assume a pixel P1'(x1',y1'),then select subsequent pixels as we work our may to the night, one pixel position at a time in the horizontal direction toward P2'(x2',y2').
Once a pixel in choose at any step
The next pixel is
- Either the one to its right (lower-bound for the line)
- One top its right and up (upper-bound for the line)
The line is best approximated by those pixels that fall the least distance from the path between P1',P2'.
To chooses the next one between the
bottom pixel S and top pixel T.
If S is chosen
We have xi+1=xi+1
and yi+1=yi
If T is chosen
We have xi+1=xi+1
and yi+1=yi+1
The actual y coordinates of the line
at x = xi+1is
y=mxi+1+b
The distance from S to the actual
line in y direction
s = y-yi
t = (yi+1)-y.
Now consider the difference between
these 2 distance values s - t.
When (s-t) <0 ⟹ s < t. The closest pixel is
S.
When (s-t) ≥0 ⟹ s < t. The closest pixel is
T.
This difference is
s-t
= (y-yi)-[(yi+1)-y]
= 2y - 2yi -1
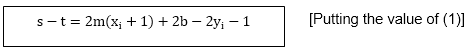
Substituting m by
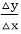 and
introducing decision variable
and
introducing decision variable
di=△x (2 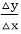 (xi+1)+2b-2yi-1)
(xi+1)+2b-2yi-1)
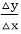 (xi+1)+2b-2yi-1)
(xi+1)+2b-2yi-1)
di=2△y.xi-2△x.yi+c
Where c= 2△y+△x (2b-1).
di+1=2△y.xi+1-2△x.yi+1+c
di+1-di=2△y.(xi+1-xi)- 2△x(yi+1-yi)
Since x_(i+1)=xi+1,we
have
di+1+di=2△y.(xi+1-xi)- 2△x(yi+1-yi).
If chosen pixel is at the top pixel T
(i.e., di≥0)⟹ yi+1=yi+1
If chosen pixel is at the bottom
pixel T
(i.e., di<0)⟹ yi+1=yi
di+1=di+2△y.
Finally, we calculate d1
d1=△x[2m(x1+1)+2b-2y1-1]
d1=△x[2(mx1+b-y1)+2m-1].
d1=2△y-△x
Advantage:
1. It involves only integer arithmetic, so it is simple.
2. It avoids the generation of duplicate points.
3. It can be implemented using hardware because it does not use multiplication and division.
4. It is faster as compared to DDA (Digital Differential Analyzer) because it does not involve floating point calculations like DDA Algorithm.
Disadvantage:
1. This algorithm is meant for basic line drawing only Initializing is not a part of Bresenham's line algorithm. So to draw smooth lines, you should want to look into a different algorithm.

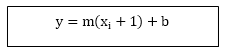
AOA
ReplyDeletemam agar hum video wali e derivation likh lain yahan jo theory main derive hua hay wo nw likhain bs thoery portion iss ka kr lain and video say derivation koi masla to nae ho ga?????
Yes you can.
ReplyDelete